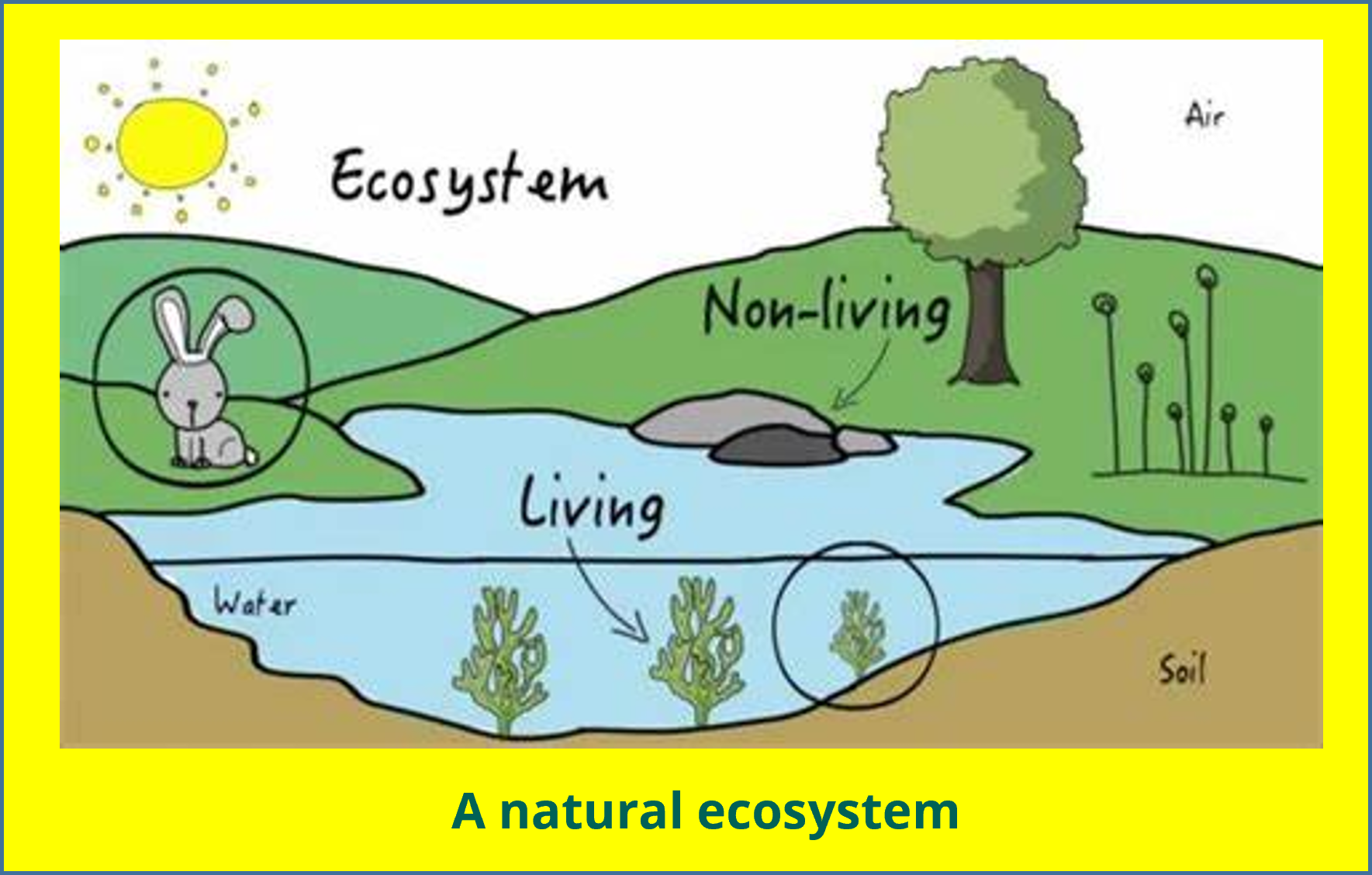
An ecosystem is a biological community of the living things (plants, animals and organisms) interacting with each other and their non-living environments (weather, earth, sun, soil, climate, atmosphere, moisture, temperature, water…). The living things are known as biotic factors and the non-living things as the abiotic factors.
Rice ecosystems are areas where rice plants are growing. Normally, depending on the hydrology glossary of where rice is grown, the rice environment can be classified into four types:




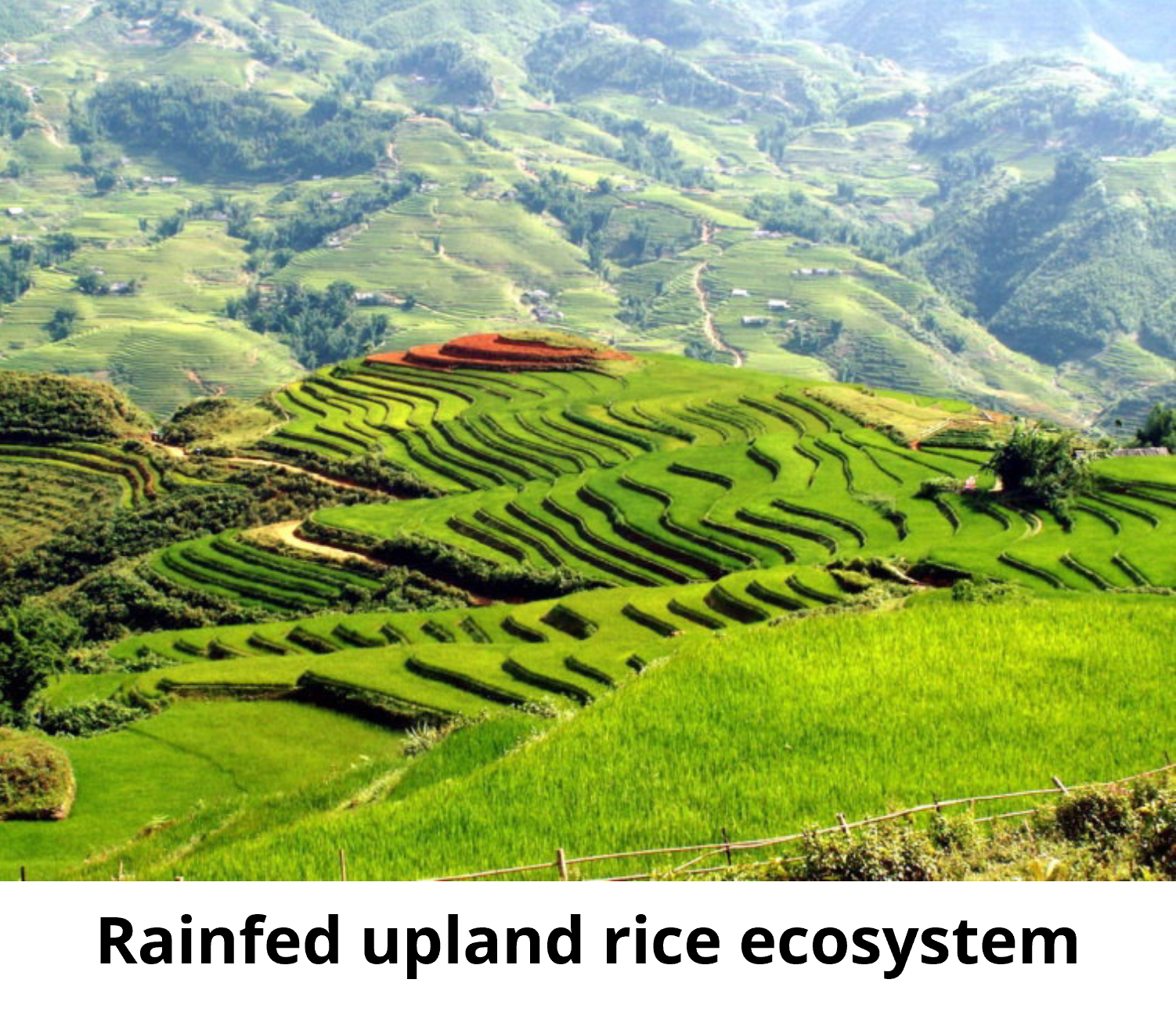
The rainfed upland rice ecosystem is cultivated in mountainous areas (under dry condition without irrigation), seeds are broadcast or dibbled into dry soil prior to the rainy season. Soil remains aerobic during all growing seasons. Usually for one crop with relatively low yield per year, many factors limit yield including drought and weeds.

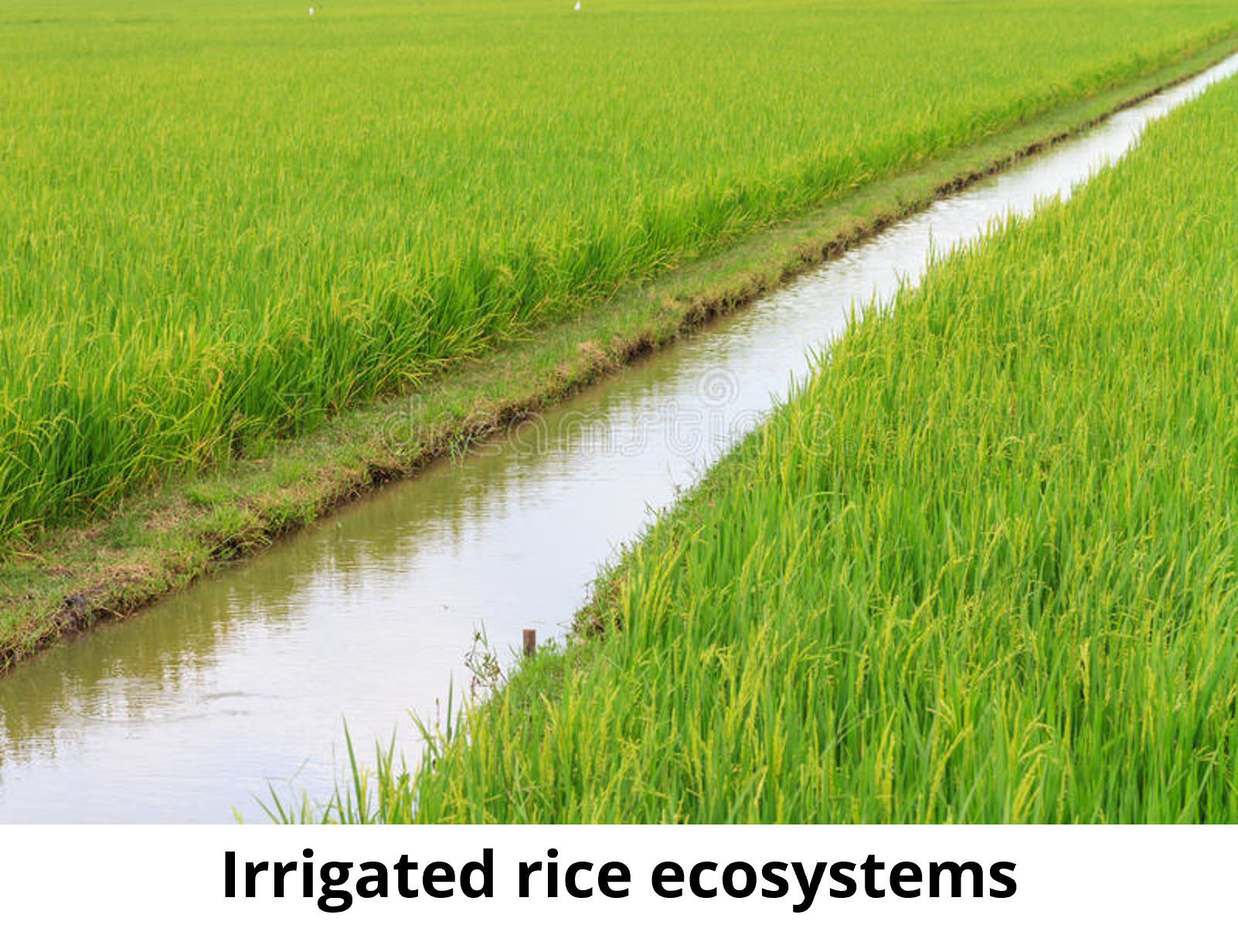
The irrigated rice ecosystems are the primary type found in East Asia. Irrigated lowland rice is grown in bunded fields with assured water supply for one or more crops per year. Availability and control of water help reduce the risk of crop failure. As a result, farmers are willing to invest fertilizers typically resulting in higher yields.

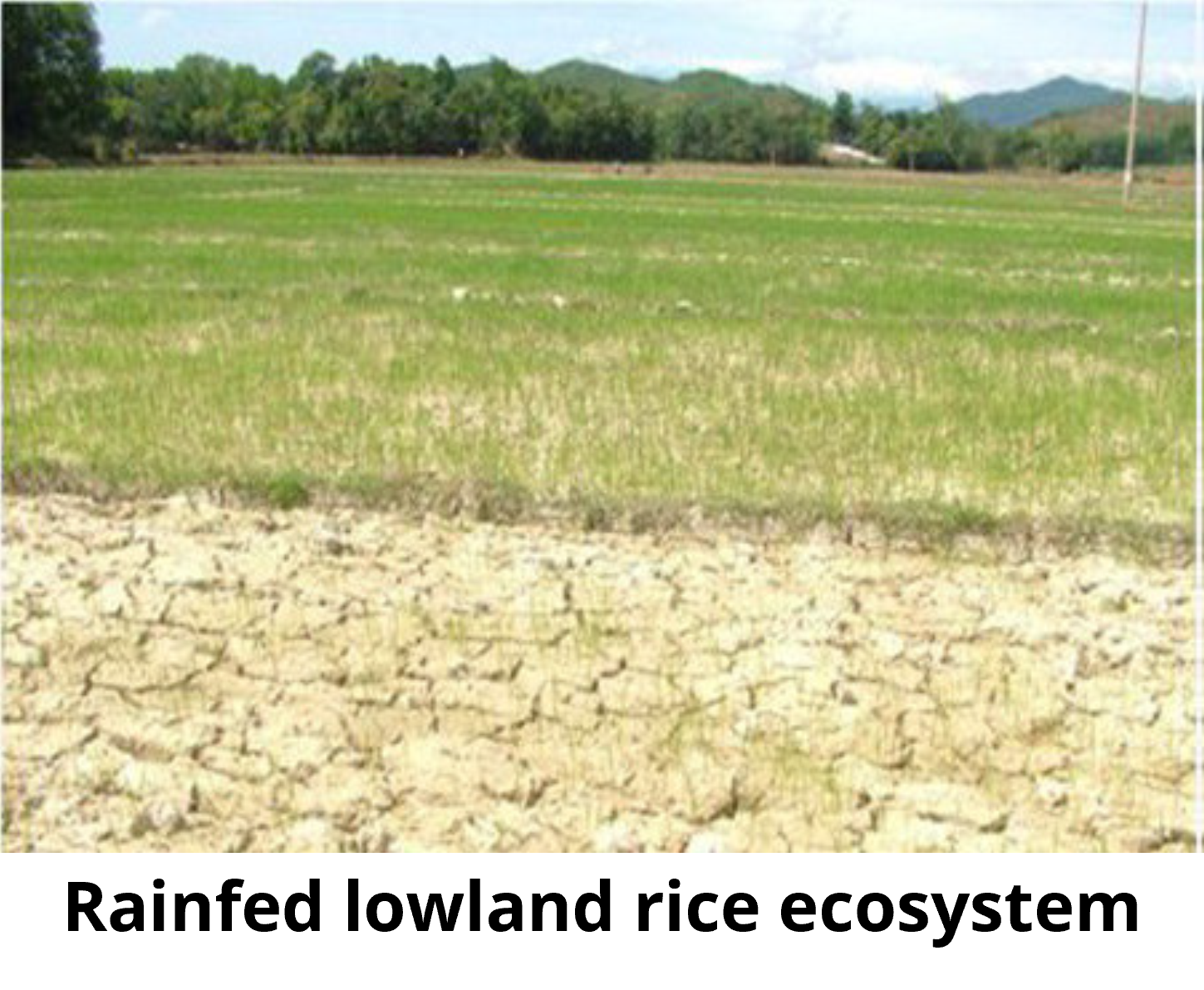
The rainfed lowland rice ecosystem may be found in similar areas as Irrigated lowland rice ecosystem. However, these areas do not have water supply and water control for irrigation. They are more prone to drought and flooding. Salinity can be a problem in coastal areas where sea water submerges the rice production area, but irrigation water is unavailable for salt removal. Rice production in these ecosystems – often hampered by drought, submergence, and problem soils – is associated with low productivity, and with a high incidence of poverty.

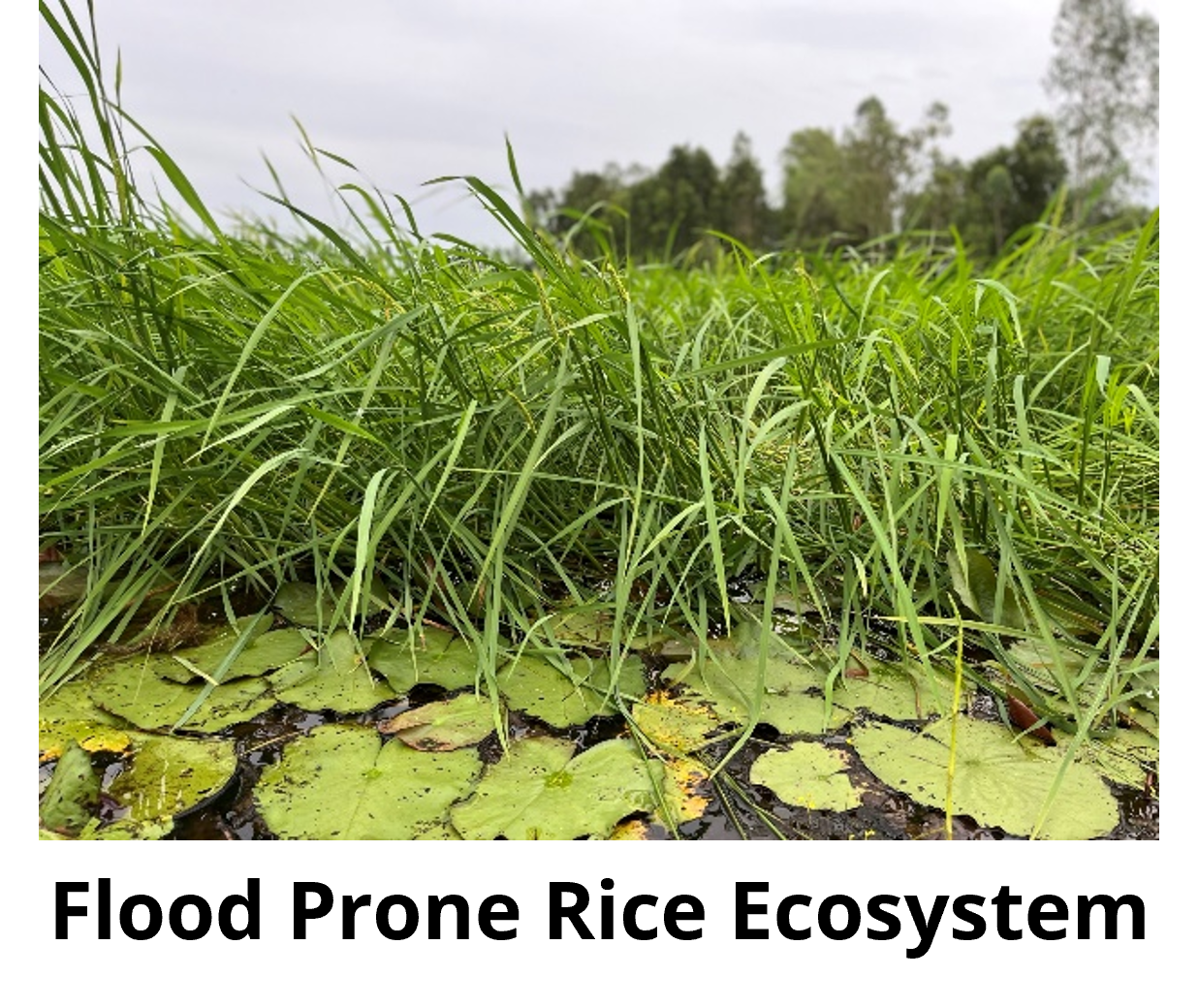
The Flood Prone Rice Ecosystems are in areas that subjected to uncontrolled floods, that occurs during the wet season from June to November. The water level may rise up to 4 m height during flooding stage. Rice varieties are chosen for their level of tolerance to submersion, called floating rice or deepwater rice with 2-3 m in long and characterized by having advanced elongation ability when raising of water. But yields are low and variable from 1 to 3 tons/ha, normally.