Major challenges and problems on rice production in SEA
- Small size/fragmented and unleveled field
- High seed rate and agrochemical overuse
- Inefficient water management
- Postharvest losses (late harvest, poor logistics and postharvest management)
- Rice straw burning and incorporation in flooded field causing nutrient lost, biodiversity loss, GHG emissions and pollutions
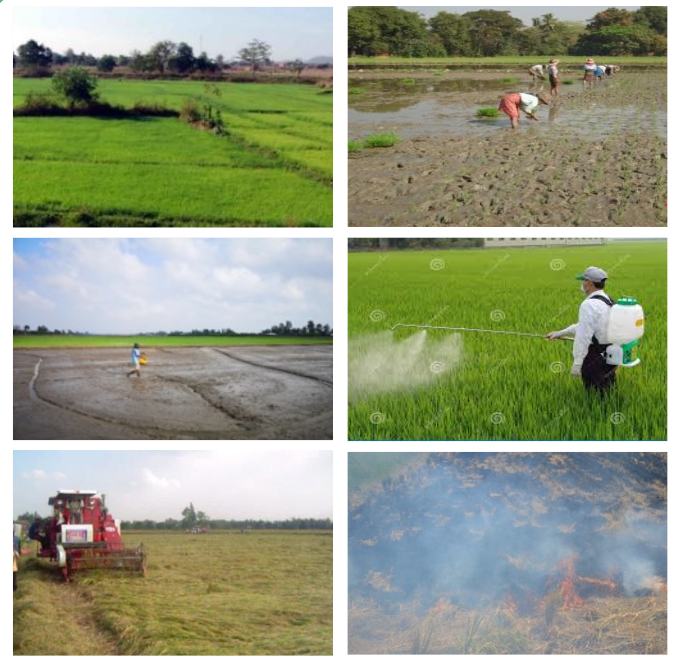

Rice postharvest losses
Rice is a living product
- Rice quality is best at harvest
- Quality deteriorates quickly over time if not handled properly
Losses occur in each operation in the PH chain
- Physical losses (loss in weight)
- Quality losses (loss in value)
Labour shortage
- High cost of PH operations
- Delays in PH operations
Best practice PH management
- Minimized losses
- Maintained quality
- Reduced cost
- Reduced environmental footprint
Physical loss (loss in weight)
- Spillage, unthreshed, pests
- In SE Asia 15-20%
Quality loss (loss in value)
- Delay in harvesting
- Delay in drying
- Spoilage in storage
- Inefficient milling
- 20-30% at market ($)

Harvesting issues 🡺 Losses
- Labor shortage – high harvesting cost
- Often delayed because of labor shortage 🡺 losses
- Poor/ low quality technologies and equipment

Harvesting loss due to poor scheduling

Drying issues and losses

Farm level and small commercial storage
- Rain, rodents, high relative humidity
- Causes huge losses
- Physical loss: >5%
- “Leakage”
- Quality
- Head rice recovery
- Discoloration
- Aroma, taste
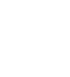
- Mycotoxins

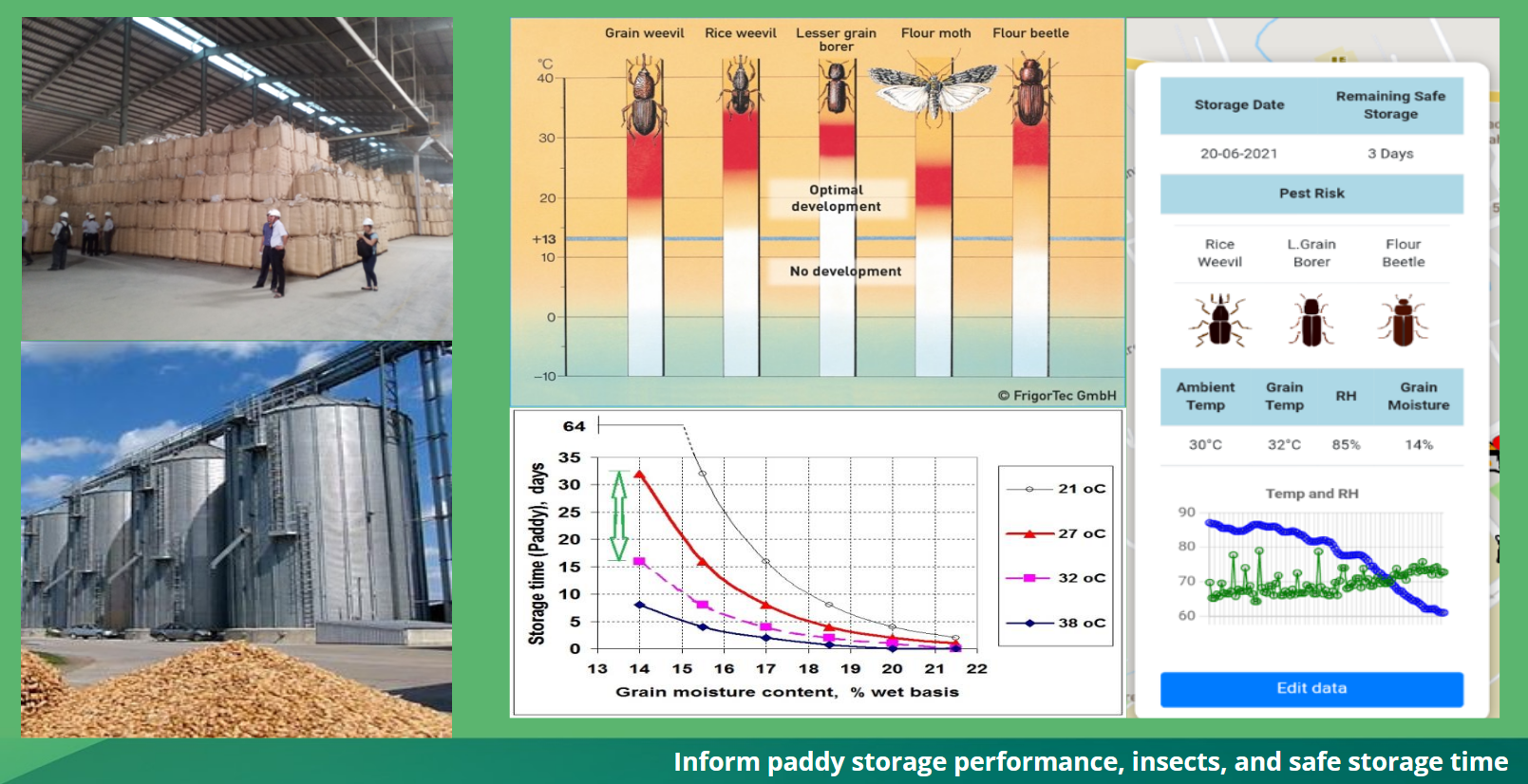
Storage problems: Microorganisms and Insects
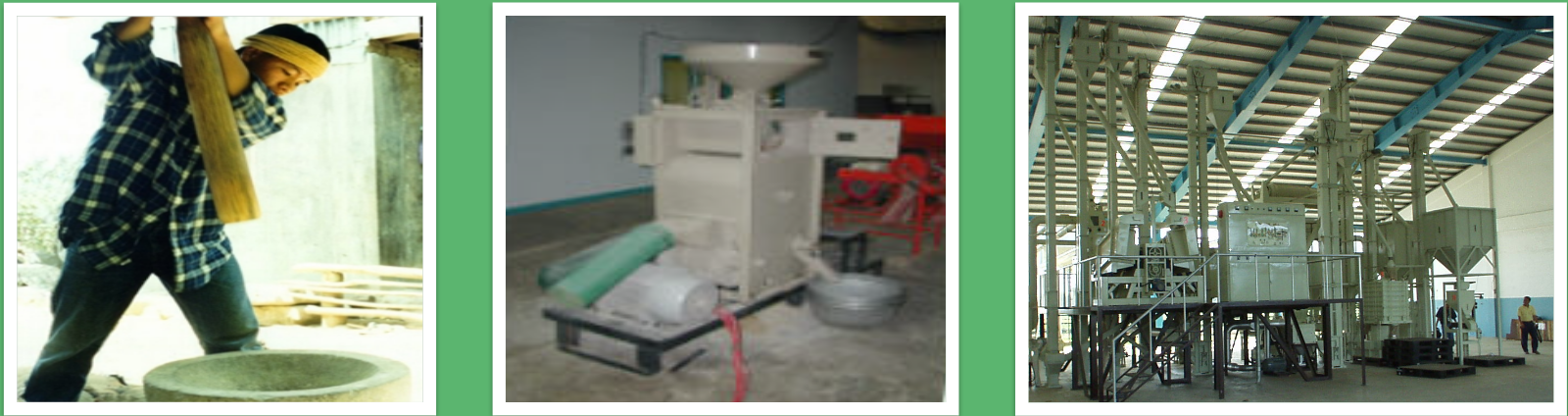
Issues of Milling
- Physical loss
- Low quality raw material
- Inefficiencies

Combine harvesting as a game changer

Previous harvesting system

Combine harvester
Some provinces in Cambodia and Vietnam now completely combine harvested
Driven by labor shortage, high collection cost

- Combine harvesters leave straw spread in the field
- Bulky (loose form: 20-40 kg/m3)
- Labor shortage during harvesting, manual collection not feasible
Rice straw: Global production >500 million tonnes/year
Problems
1) Burning > 50%
- Nutrient lost
- GHGE and pollutions
- Biodiversity loss (soil-dwelling organisms such as fungi, bacteria and rotiferal)
2) Incorporation of rice straw in the flooded field >30%
- CH4 (1 CH4 = 28 CO2-eq)
- methane toxicity, black root diseases

Solutions
- Scale-appropriate and sustainable technologies/solutions (affordable, scale-suitable, highly efficient, economically viable, low carbon footprint)
- Capacity development and business models for scaling
- Farmer perception/behavioral change

Mechanization for increased farming efficiency and low carbon rice production
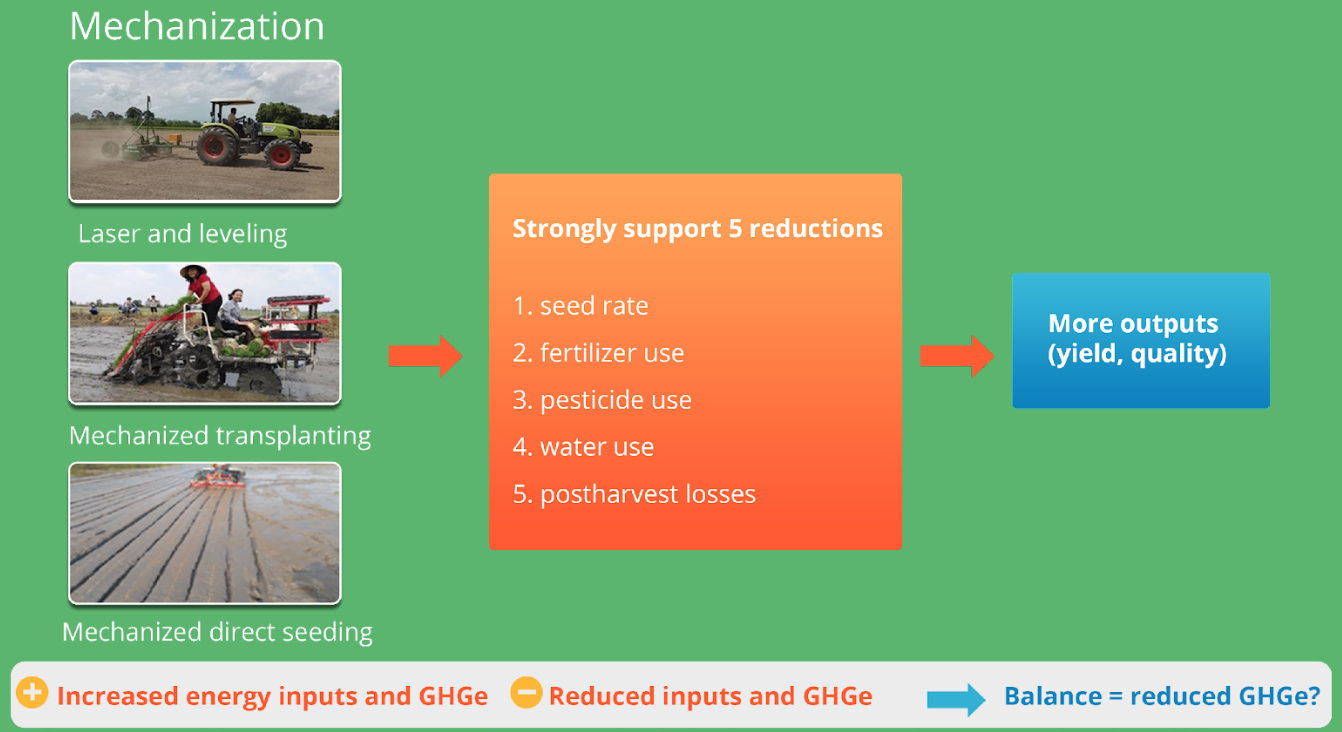
Laser land leveling: Precise leveled field for optimized water and crop management
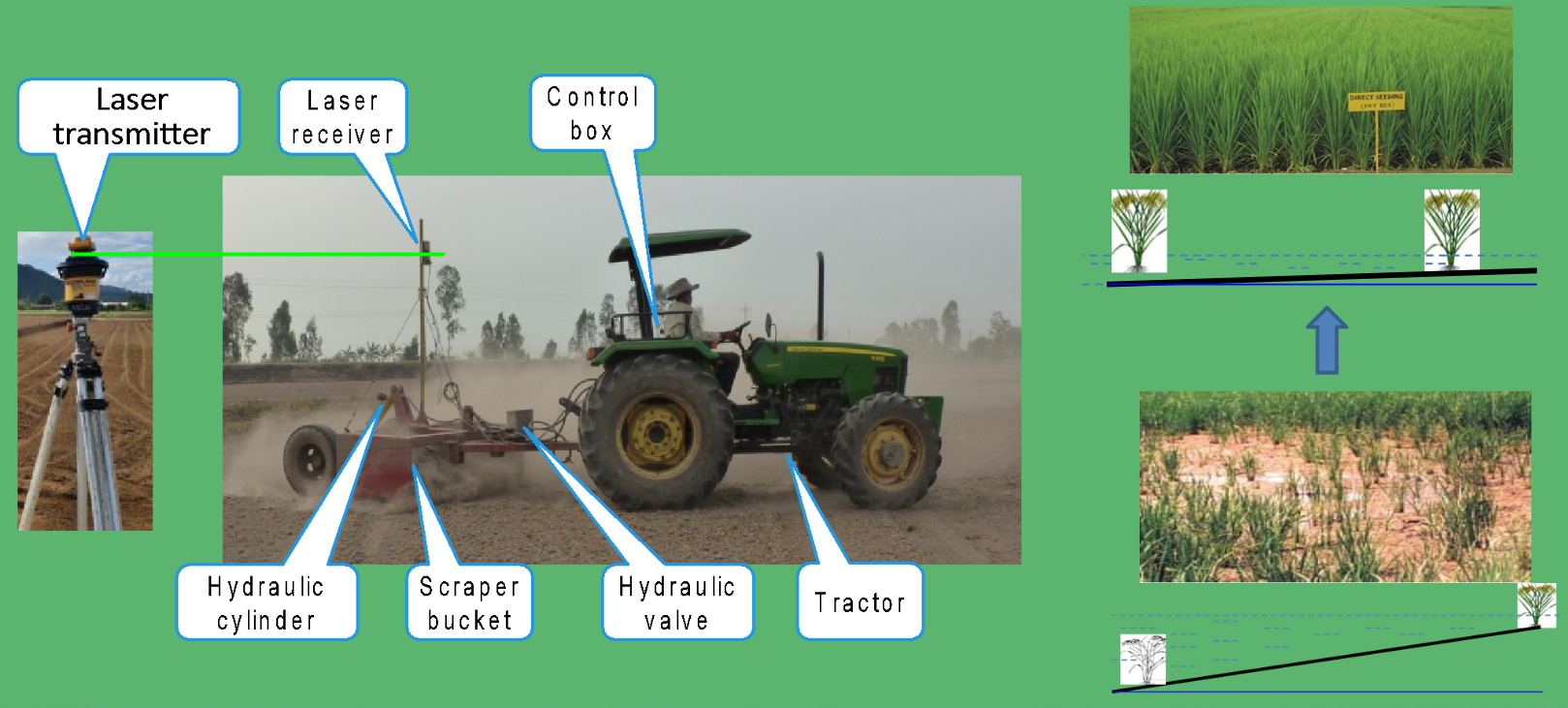

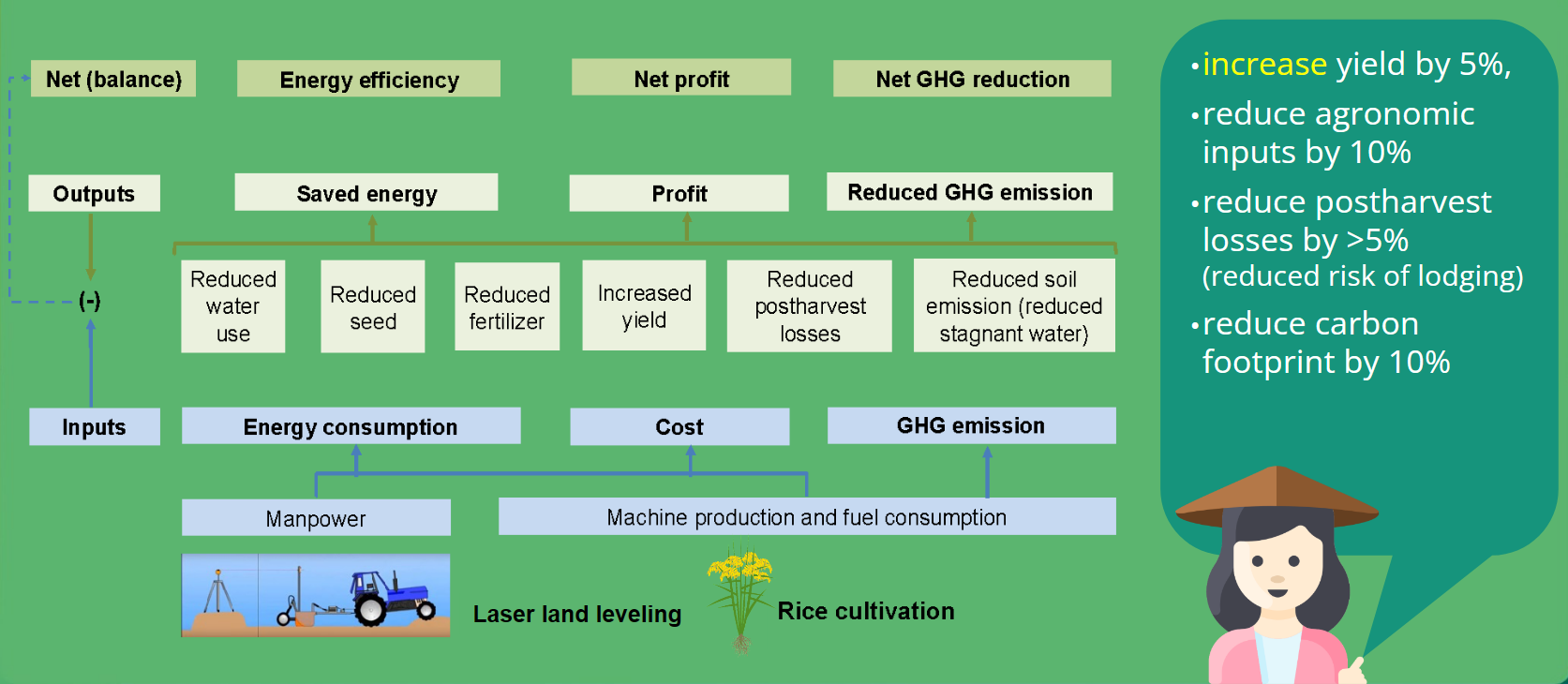
Mechanized and precision direct seeding

Example: Dry Dsr, India
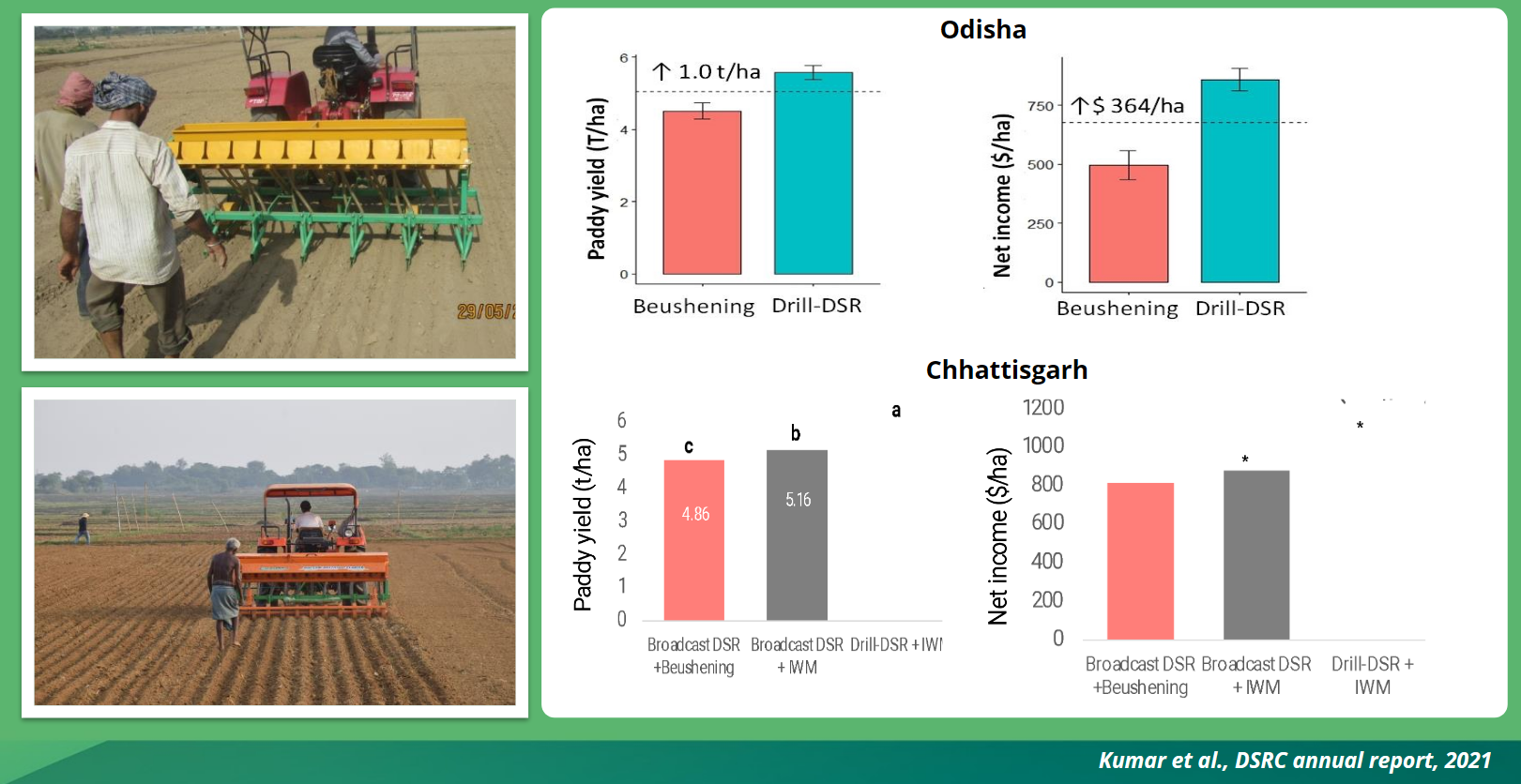
Example mechanization and carbon footprint reductions
Mechanized direct seeding
- Reduce seeding rate >50%,
- Reduce fertilizer use > 20%,
- Reduce risk of pest/ diseases and lodging
- Increase yield about 5%
- Reduce carbon footprint >10%

Integrated mechanization and precision solutions to increase farming efficiency

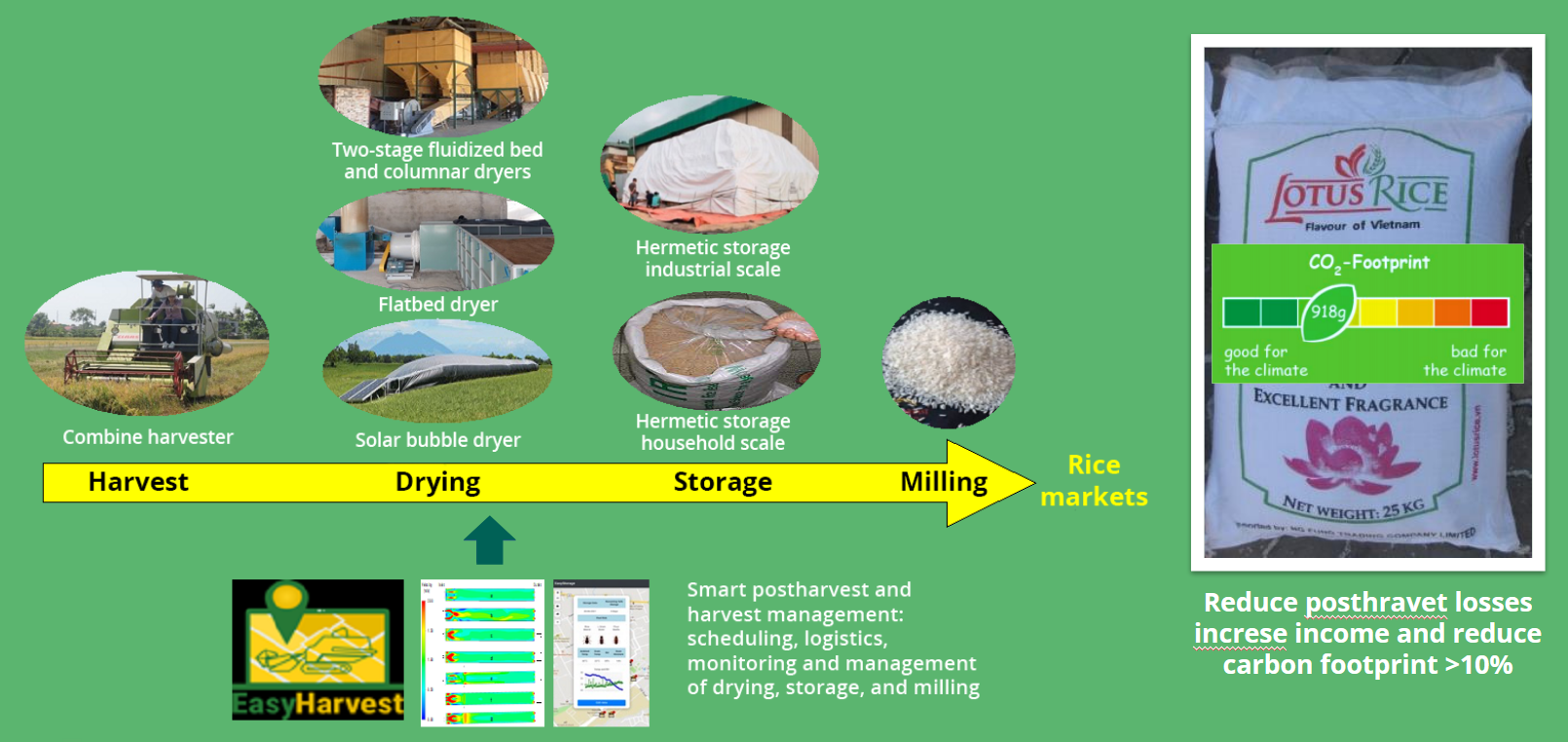
Post harvest management to reduce postharvest losses and carbon footprint
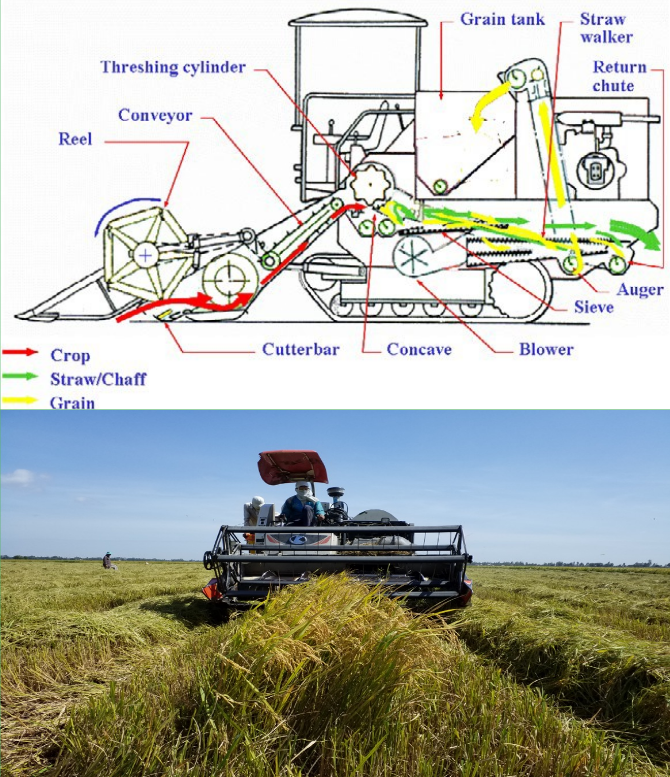
Harvesting
1) Timing of harvest
When 85% (+-2%) color of grains per panicle are straw or yellow
2) Using combine harvesters
- Combine cutting, threshing, cleaning, and sacking
- Address problems caused by labor shortage
- Significantly reduce losses compared with manual harvesting (avoid losses caused by delay of harvesting, transportation of rice plants between cutting and threshing, etc.)
Drying and storage
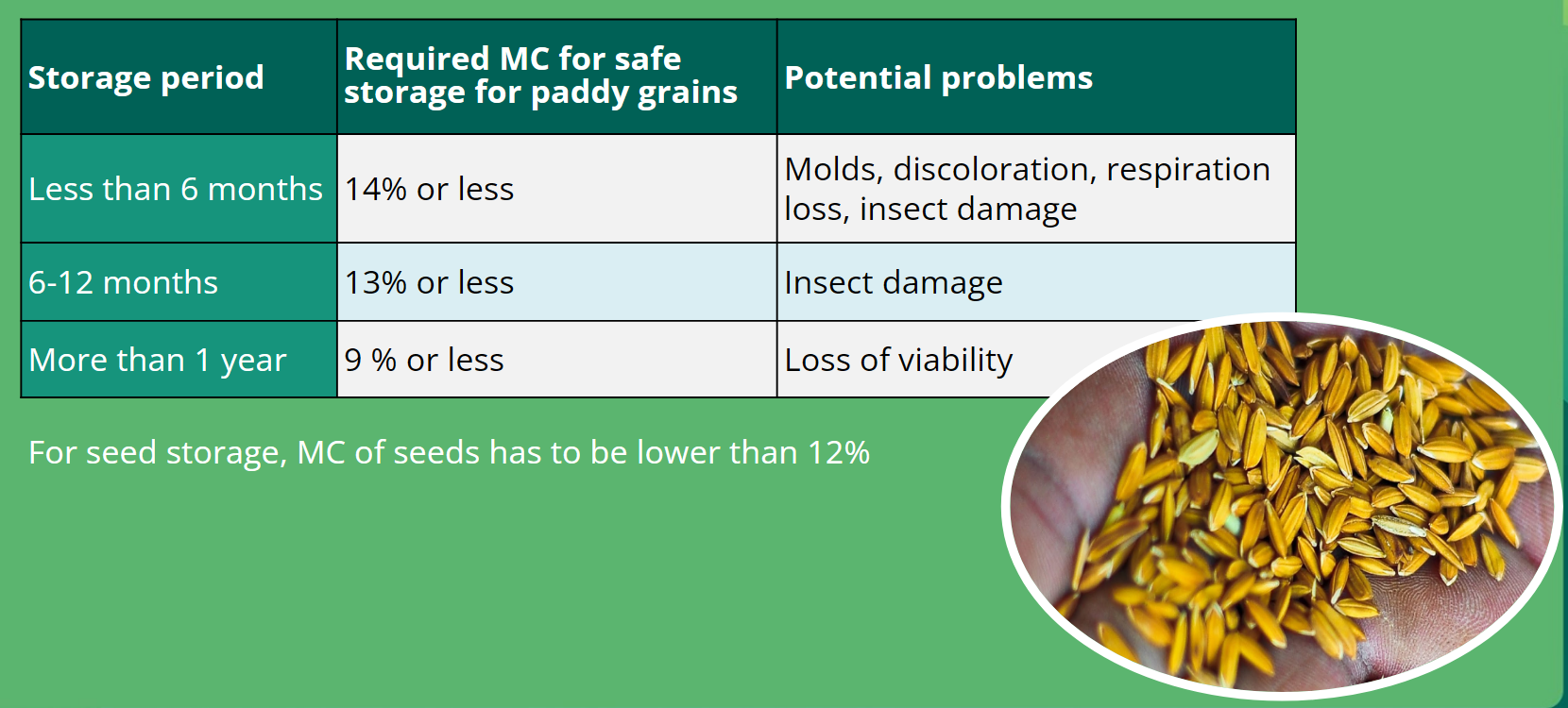
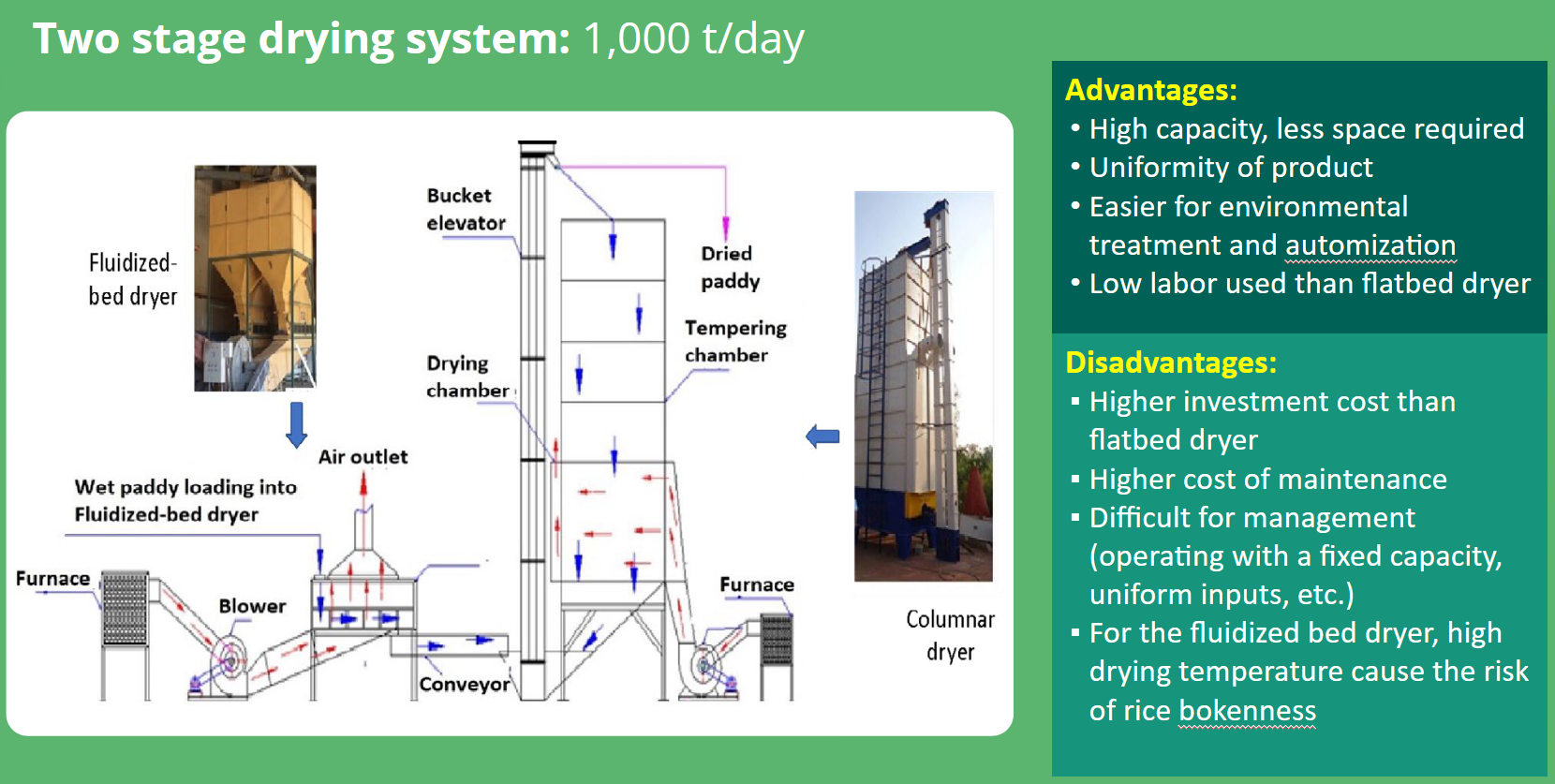
Drying (from small to industrial scale)

Solar bubble dryer (sbdtm) (irri, garinpro, and hoheihem university)
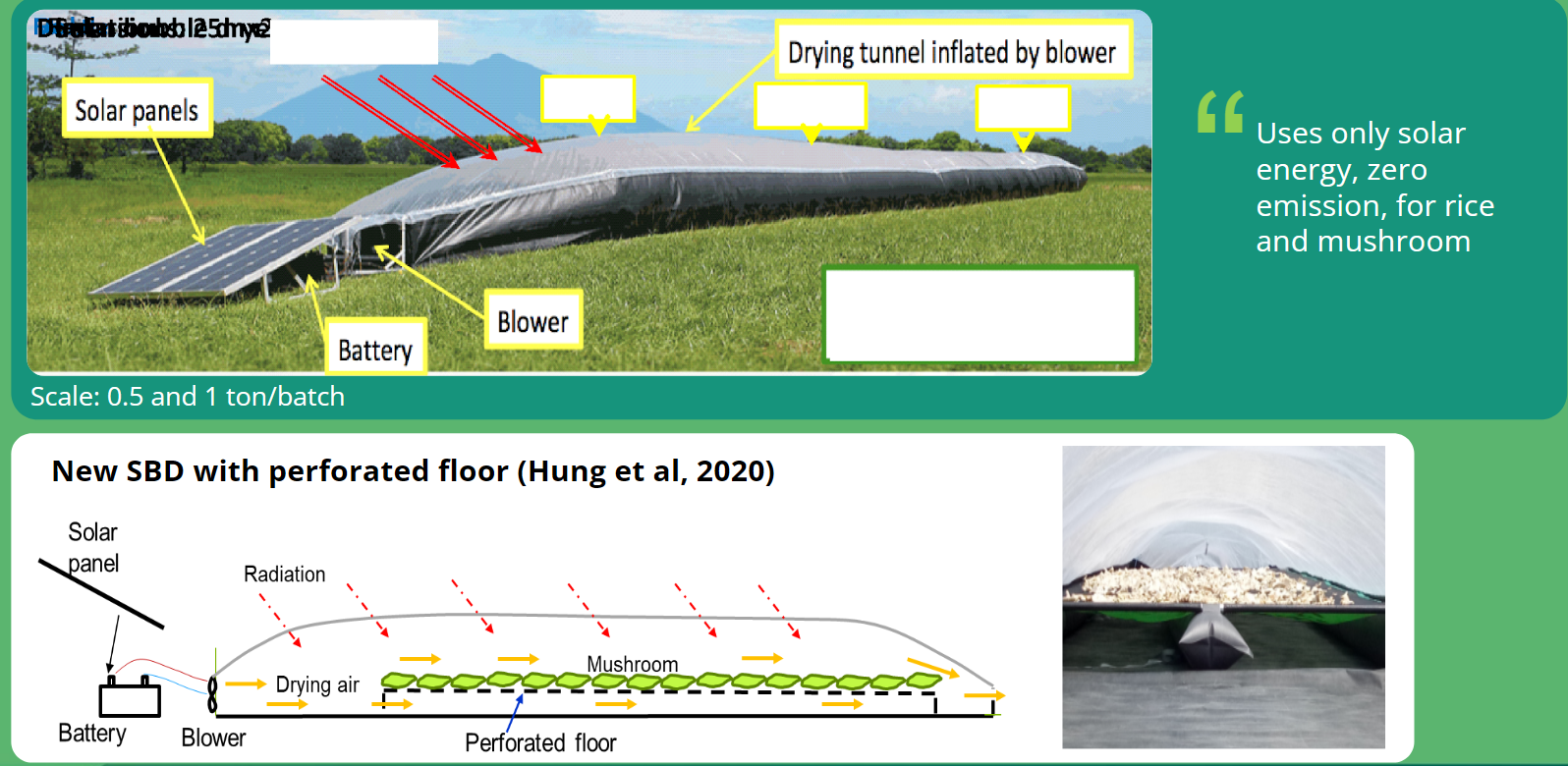
Inflatable solar bubble dryer features

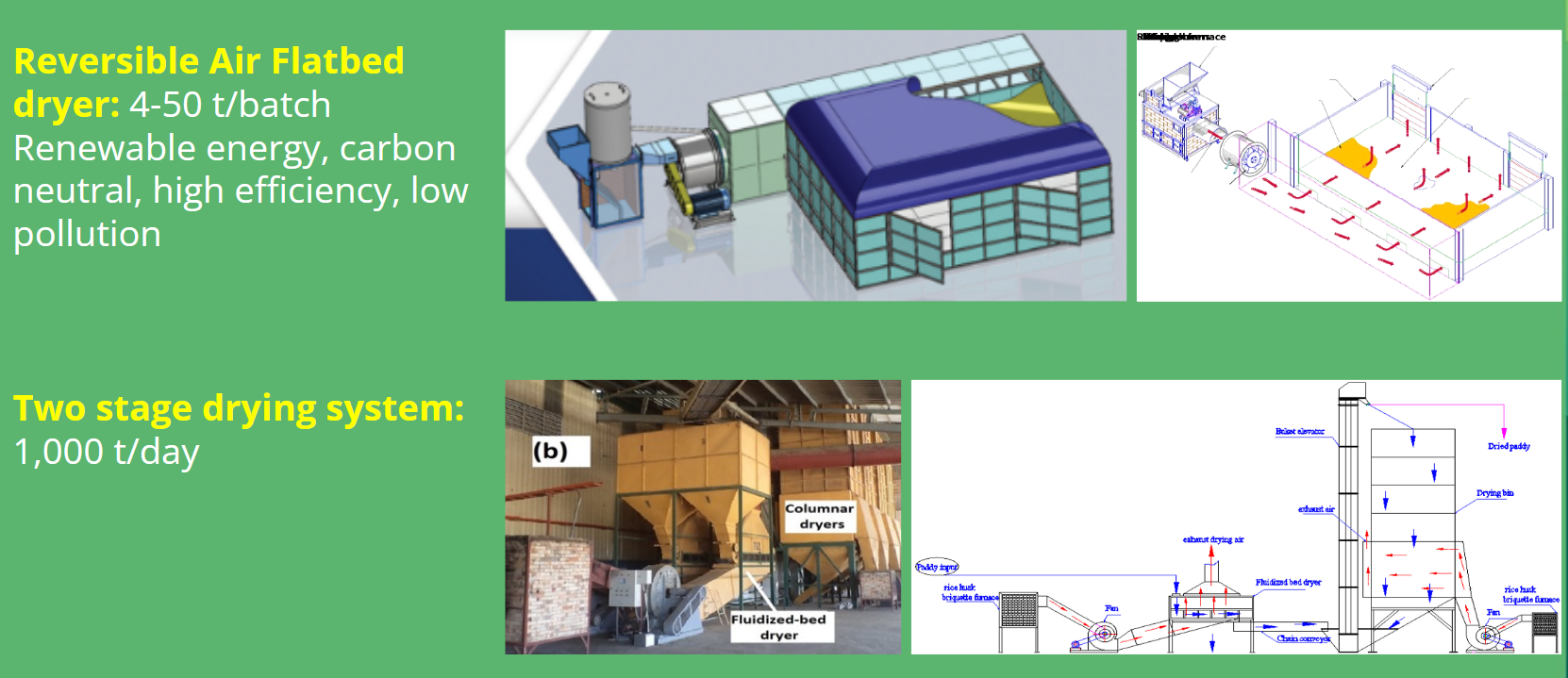
Flatbed dryer
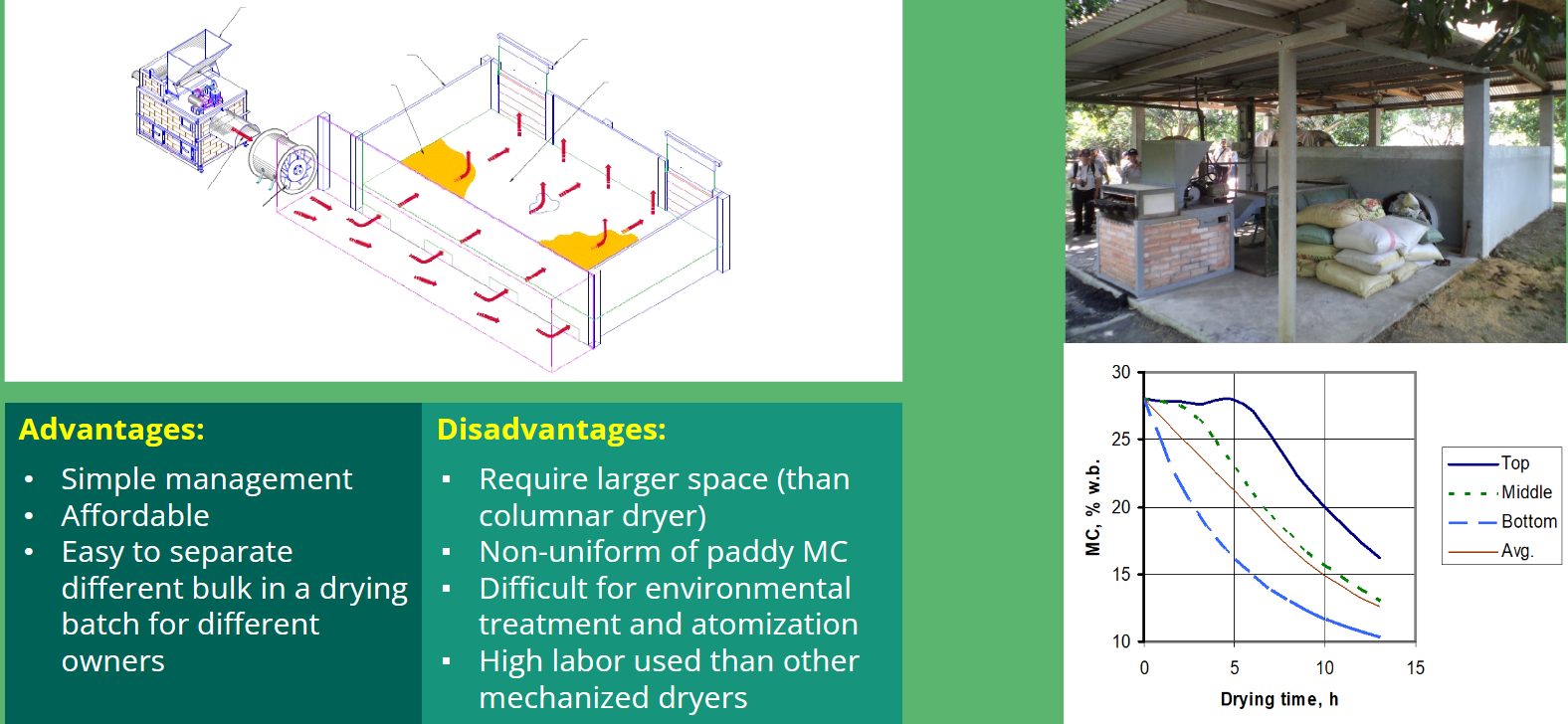
Reversible air flatbed dryer
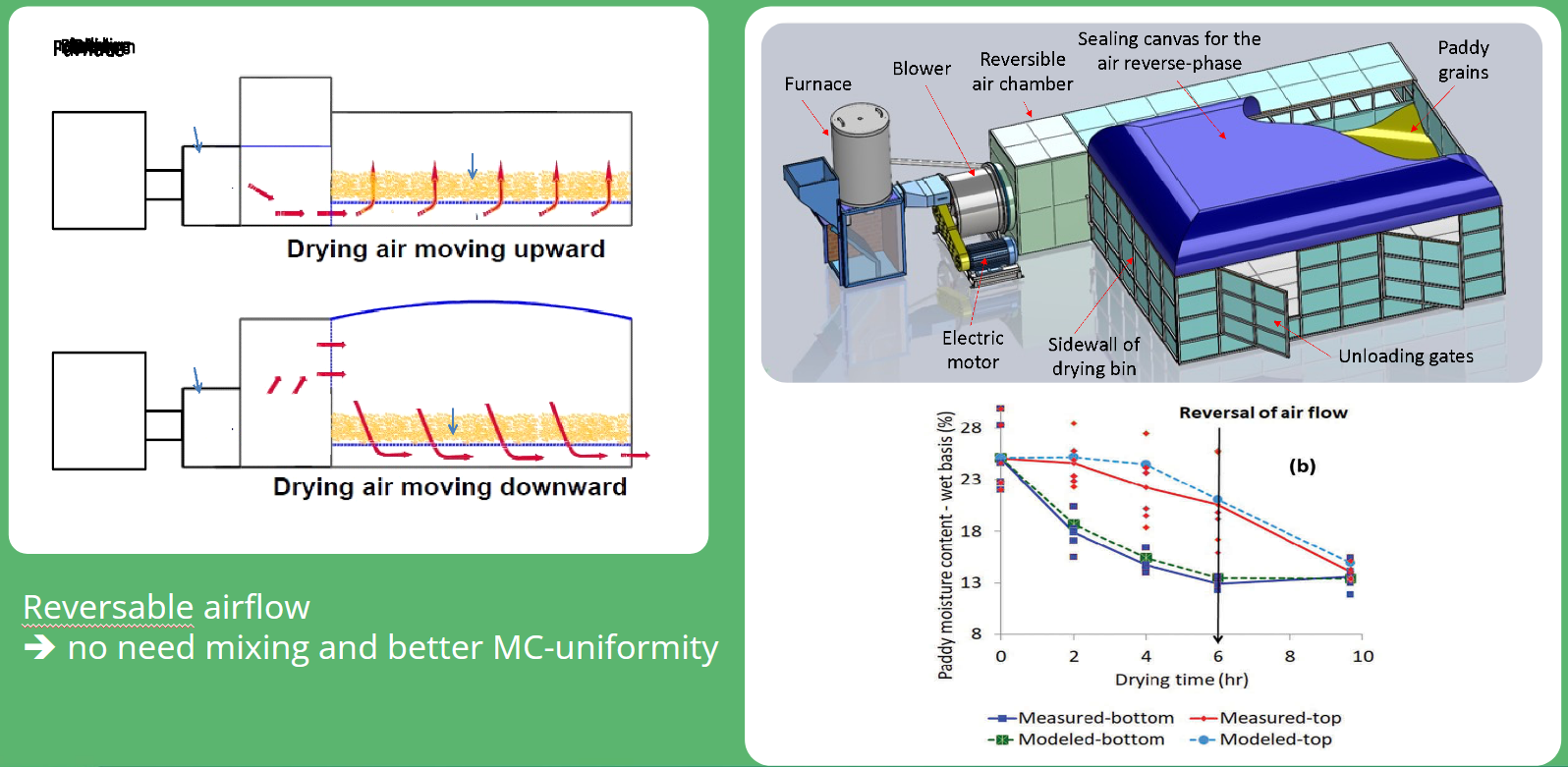
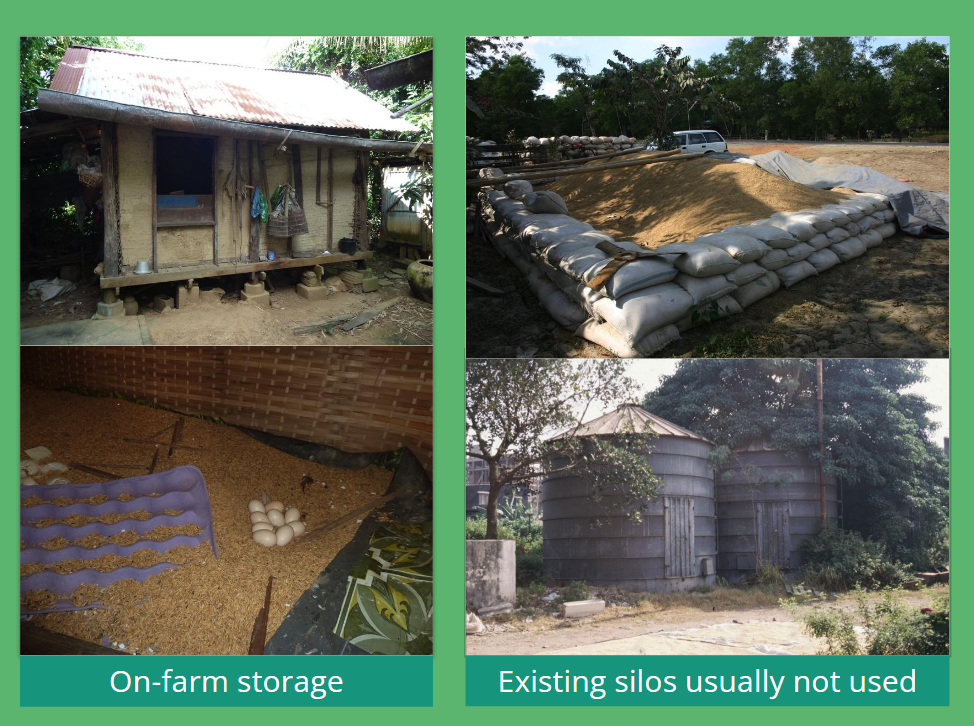
Storage systems
- Fixed Installations
-
- Warehouse
-
-
- Bag or bulk
-
-
- Indoor silos
-
-
- Bulk
-
-
- Outdoor silos
-
-
- Bulk
-
- Flexible
-
- Hermetic storage
- Bag or bulk
- Hermetic storage
-
- Silo bags
-
-
- Bulk
-
-
- Bunker storage
-
-
- Bulk
-

Hermetic sealed storage systems
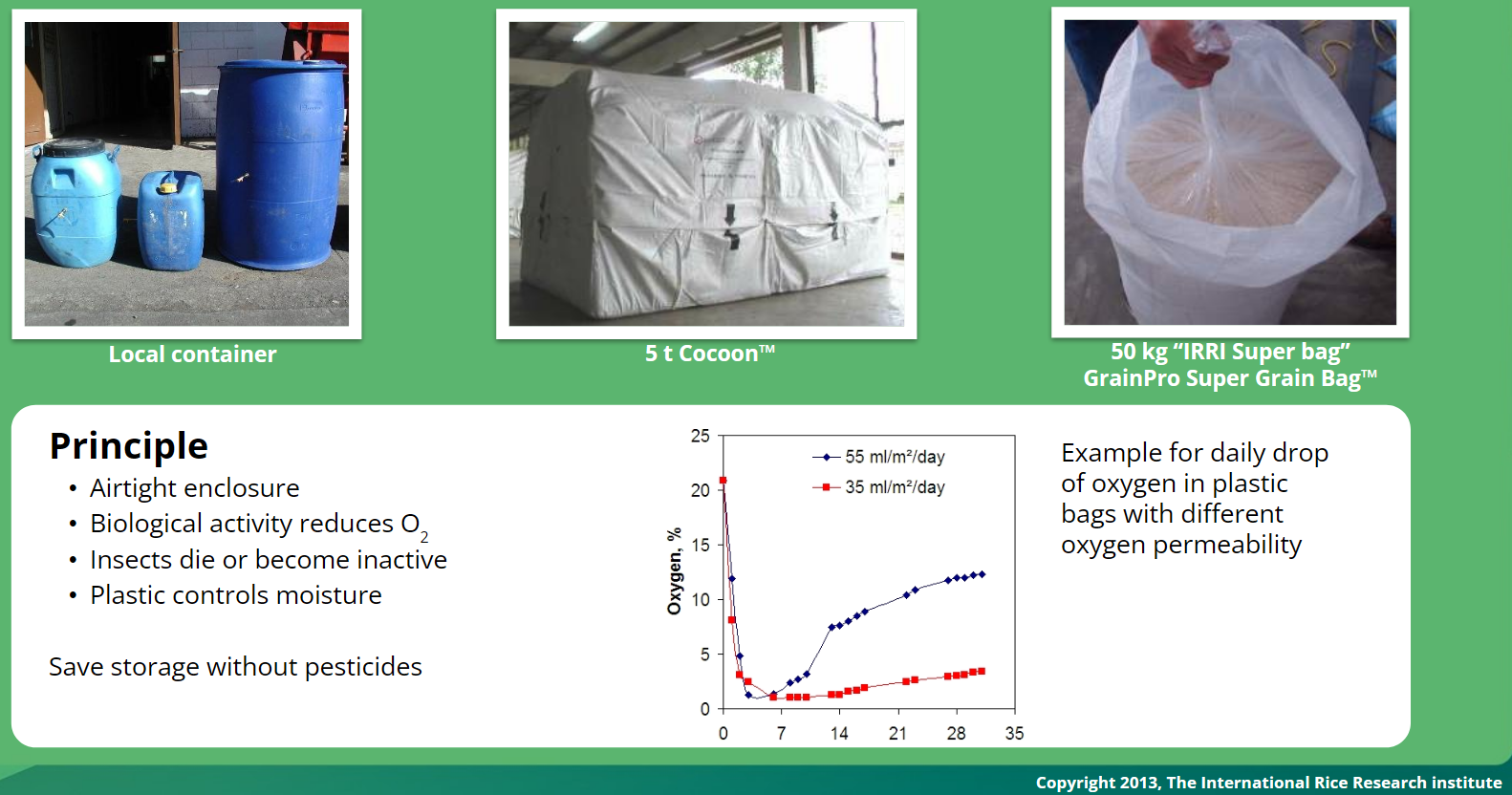
STORAGE (IRRI and Grainpro)

- Hermetic Storage (small and industrial scales)
- Maximized maintenance of grain and seed quality
No energy consumed, no pesticide used - Satisfy one of the critical requirement of the Sustainable Rice Standards

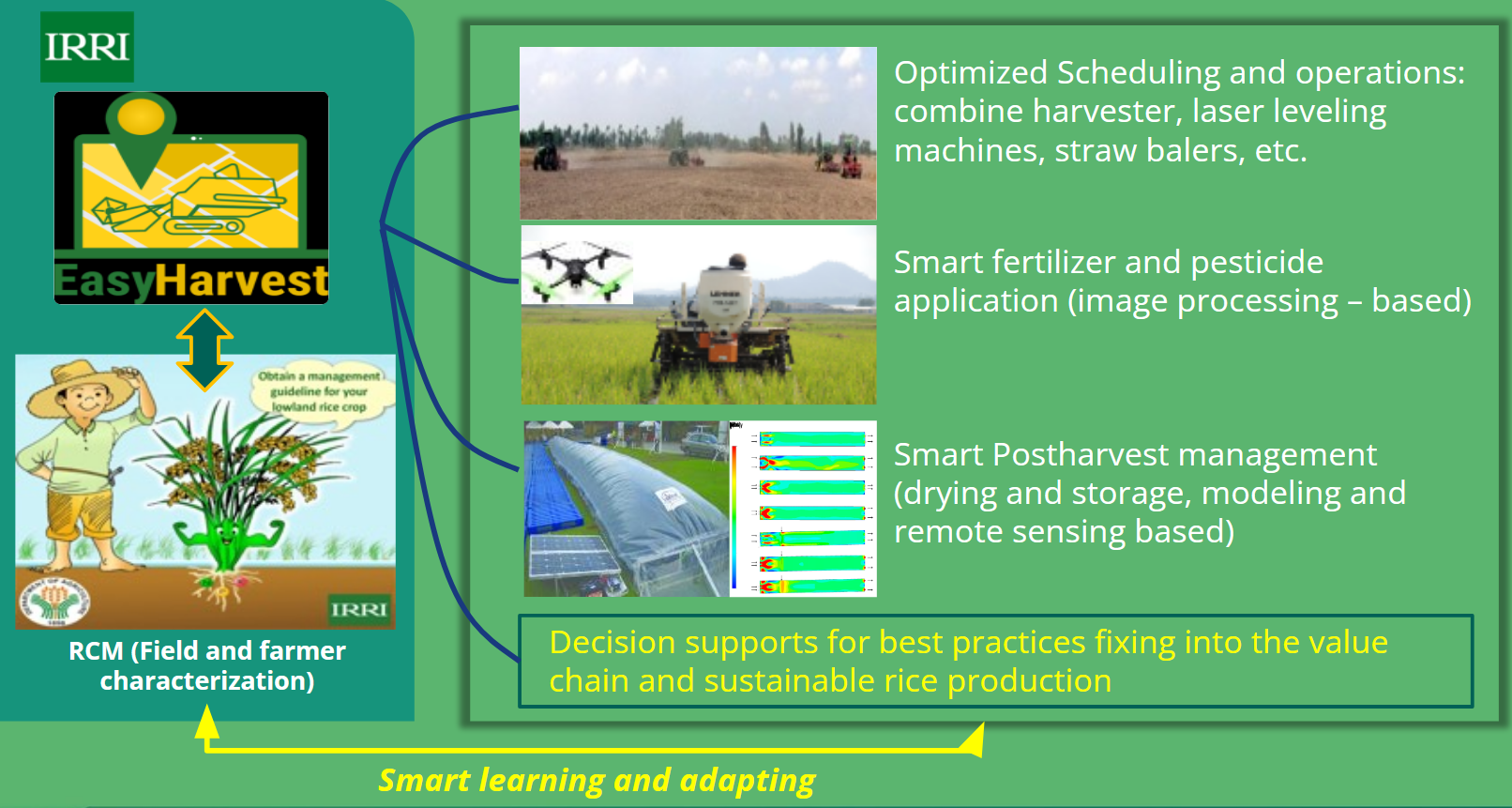
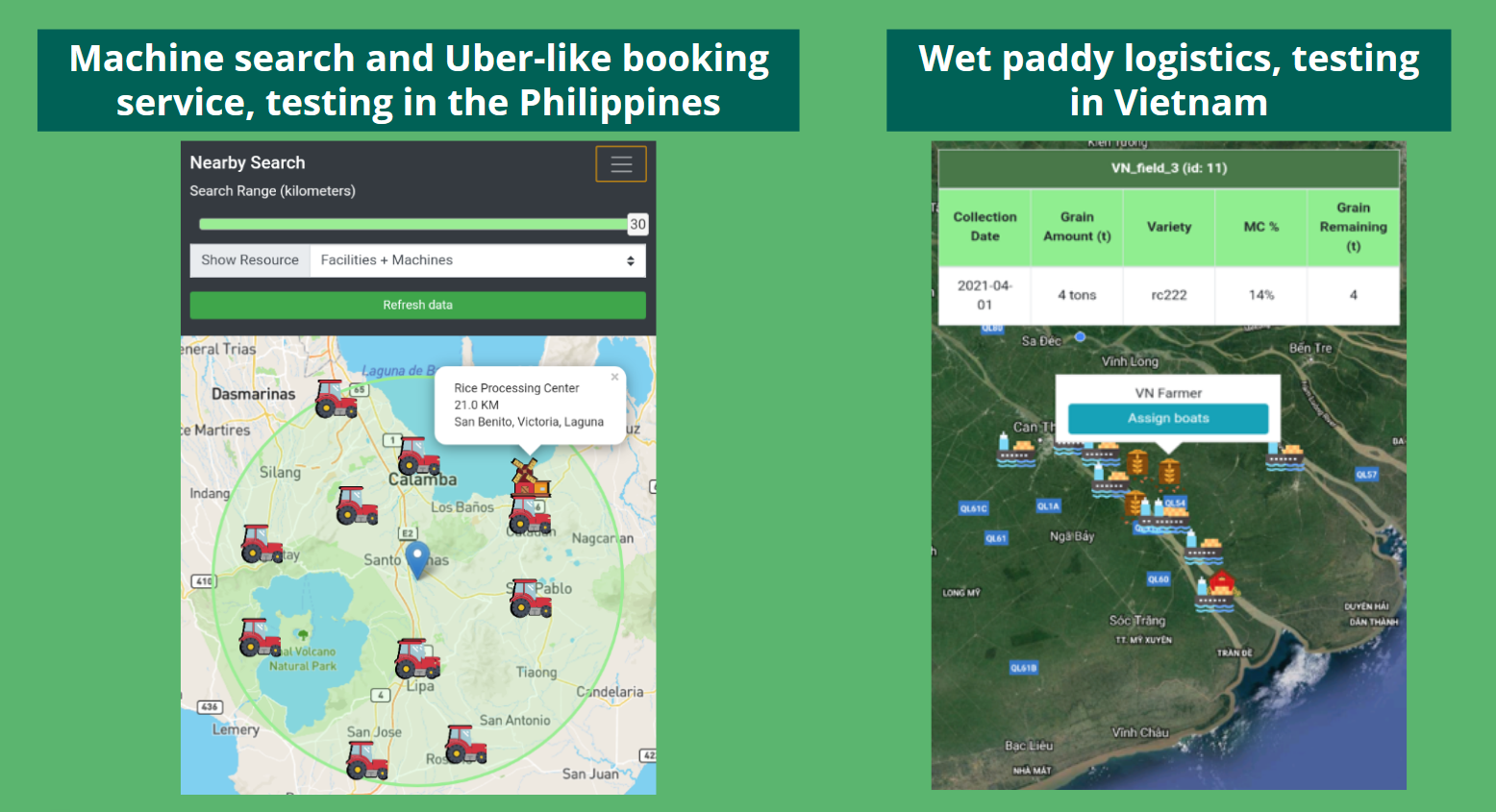
Easyharvest piloted in vietnam for smart storage management