Step 1: Site Preparation
- Straw mushrooms can be cultivated in shaded, well-ventilated areas or under direct sunlight, such as on-field ground or seedbed ground. The growing site must have good drainage to prevent waterlogging during irrigation or rainfall.
- The soil for straw mushroom cultivation should be treated with lime at a rate of 5 kg/100 m2 (300-500 kg/hectare).

Step 2: The straw Source
The straw sources can be in either bale or loose form. The straw must be disease-free, not affected by pesticides, not contaminated with salinity, white mold, or rot rotten due to rain.

Step 3: Preparing the soaking tank
- Prepare the soaking tank (locating the tank near the composting area is advisable for convenience).
- Use a waterproof tarpaulin to construct a soaking tank with dimensions of approximately 2.5 x 4.5 meters (or adjust according to the actual scale).
- The ground for setting up the soaking tank must be level and free of sharp objects that could damage the tank’s walls.

Preparing a lime solution
Soak the straw in the tank, trampling it to ensure even absorption. After soaking for about 10 minutes, remove the straw and allow it to drain

Step 4: Composting and Turning the Compost Pile
- Place the straw on an iron/bamboo rack (20 cm above the ground) or on a well-ventilated ground surface.
- Place banana trunks in the center of the compost pile to improve aeration.
- The amount of straw used is at least 100 kg, and the dimensions of the compost pile are approximately 1.2 to 1.5 meters high, at least 1.5 meters wide, and more than 1.5 meters long
- Cover the compost pile with a waterproof tarpaulin, ensuring that there are ventilation holes on top.

- Monitor the compost moisture and add water if necessary, ensuring the temperature remains above 60-70°C.
- After 7 and 17 days of composting, turn the pile for the first and second time, respectively, moving the material from the inside out and then from the outside in.

Step 5: Preparing Mushroom Spawn
- The mushroom spawn is rice husk spawn. Choose bag of spawn with a uniform white mycelium growth and a pleasant smell.
- The spawn is separated and mixed with mycelium stimulating yeast at the recommended ratio. Or mix with vermicompost, dose of 70-160g and mushroom mycelium stimulating ingredients as recommended.

Step 6: Putting compost in bed
- After composting for 16-18 days, the compost is placed in a bed. The size of the compost bed should be 35-40 cm wide and 35 cm high. Straw is taken from the compost pile, rolled, and arranged into lines
- Following this, a layer of spawn is spread in the middle of the line (approximately 160g/m of line).
- Then the surface is covered with another layer of straw
- The compost bed is then prepared and watered. Using both hands, the compost bed is stroked and tightly compressed. Subsequently, the compost bed is exposed to direct sunlight for 4 days.

Note: Using the tarpaulin cover the compost bed is used in the rain; make sure the ventilation is good. In case it is windy, arrange the compost line to avoid the direct wind, the wind

Step 7: Caring and Watering
- After drying in the sun, the bed should be covered with straw. Then the cover should be wetted.
- Watering once daily, either in the afternoon at about 4 pm or in the morning (7-8 am), should be done using a shower.

- After covering the straw for 4 or 5 days, check the spread of mycelium and turn the bed cover to limit the mycelium spreading beyond the cover layer.
- When the mycelium spreads evenly on the 7th or 8th day, begin watering for mushroom growth. About two days later, the pins will start appearing.

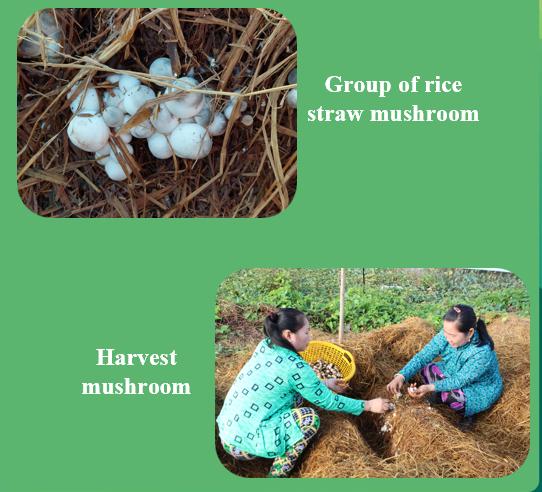
Step 8: Harvesting
- The time from sowing spawn to harvesting is about 12 days. Harvest twice a day, in the morning (at 5-6 am) and in the afternoon (at 5-6 pm)
- There are 2 harvests. The 1st harvest is within 4 days. Afterward, take care of the mushroom bed, and the mushrooms will appear approximately 5-6 days later.
- How to harvest mushrooms: Gently rotate the mushroom to separate it from the compost bed. Do not leave the mushroom feet on the compost bed, as they will rot and damage the affected mushroom buds. After harvesting, cover the compost bed.

Step 9: Cleaning after mushroom cultivation
- After harvesting the mushrooms, the substrate can be composted to create organic fertilizer for plants.
- Use burnt lime to disinfect the growing area and leave it in the sun for at least 1 month before growing the next crop.